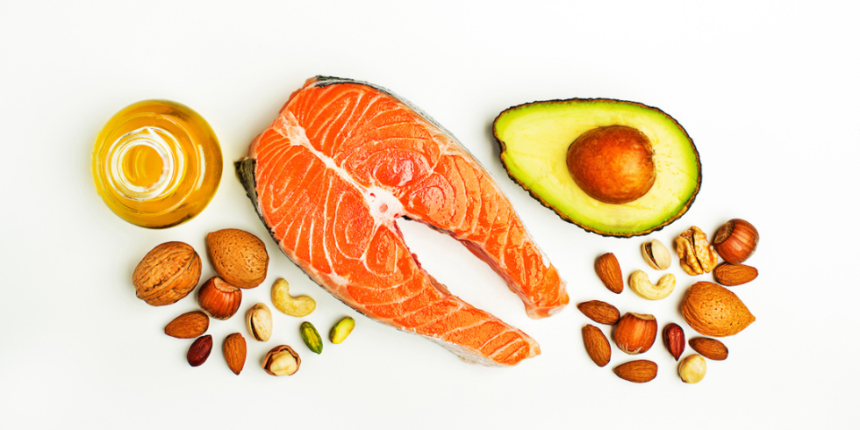
As a more informed consumers, we have traveled a long way from anti-fat rhetoric that has permeated nutritional space for a few years. We now know that fat is a important part a balanced diet and fatty acids like omega-3s are beneficial for our health.
But what are the fatty acids exactly and are they the same as fats? Why are they good for us? Here’s what you need to know.
What are fatty acids?
Fat acids are carboxylic acids that consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms and serve as fat construction blocks. They contribute to the support of the cell membrane, long -term storage of fuel and hormonal and metabolic signaling.
Depending on their chemical structure, fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated, explains Brittany Linn, DR, CDN, owner of B. Nutrition Linn in New York.
Saturated fat comes from animal products such as meat, eggs and cream, as well as certain plants based on plants. Because saturated fats have a negative impact on heart health, the American Heart Association recommends limiting the intake of saturated fat to around five of your total daily calories.
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), On the other hand, are often called “healthy fatAnd are supposed to have beneficial effects on our overall health.
There is more than 20 types Fat acids found in food, but three in particular obtain most of the media threw for their health benefits: omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 and omega-9.
Types of fatty acids and their advantages

There are three main types of unsaturated fatty acids: omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids. The number of the name of each refers to the place where the double bond is located on the chain of fatty acids, explains Linn. (Don’t worry, we will not transform this into a chemistry lesson.)
Omega-9 fatty acids are a type of mufa. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are types of PUFA, and both are considered to be a healthy diet.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are considered “essential” Because our body cannot create them, which means that we must get them from food sources. Omega-9s are non-essential because our body can make them alone.
Here is what you need to know about each type of fatty acid.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated and mainly come from Plants and fish. The types of omega-3 include eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). In addition to a lower risk of certain emotional and cognitive conditions, omega-3 fatty acids are associated with better Heart and Eyes Health.
Omega-6 fatty acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are also polyunsaturated. While omega-6 are common in the standard American diet, the one you should pay attention is linoleic acid, which, with omega-3, has been linked to improvement heart And brain health.
Omega-9 fatty acids
Omega-9 fatty acids are not as often as often as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Although they are not essential, omega-9 fatty acids would have many health benefits, so it’s always a good idea to integrate them into your diet.
How many fatty acids should you consume?
Fats are an important element of a healthy diet. Individual needs can vary, but around 30% of your calories every day should come from fat. (The remaining 70% would come from proteins and carbohydrates.) Ideally, the majority of these 30% will come from healthy fats – like the omega mentioned earlier – while limiting saturated fat and avoid completely trans fatty.
Best sources of fatty acids

In many foods, omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids are all present-so the list below is based on fatty acids they contain the most, says Linn. The three types of fatty acids are beneficial, but keep in mind that omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 cannot be produced by your body, so it is particularly important to obtain food sources.
Omega-3 sources
- Fish and other seafood (especially Gras in cold water like salmon, sardines, herring and mackerel)
- Flax seeds and linseed oil
- Chia seeds
- Walnut and walnut oil
Omega-6 sources
- Grape oil
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Walnut and walnut oil
- Firm tofu
- Sunflower seeds
Omega-9 sources
- Olive oil
- Cashew oil
- Almond oil
- Avocado oil
- Peanut oil