Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content covering cutting-edge AI. Learn more
Chinese AI startup DeepSeek, known for challenging major AI vendors with its innovative open source technologies, today released a new ultra-large model: DeepSeek-V3.
Available via Cuddly face According to the company’s licensing agreement, the new model comes with 671B settings but uses a blended architecture of experts to enable only certain settings, to handle given tasks accurately and efficiently. According to benchmarks shared by DeepSeek, the offering is already at the top of the charts, outperforming major open source models, including Meta Llama 3.1-405Band closely matching the performance of Anthropic’s and OpenAI’s closed models.
This release marks another major development bridging the gap between closed and open source AI. Ultimately, DeepSeek, which began as an offshoot of China’s quantitative hedge fund High-level capital managementhopes that these developments will pave the way for artificial general intelligence (AGI), where models will have the ability to understand or learn any intellectual task that a human being can perform.
What does DeepSeek-V3 bring?
Just like its predecessor DeepSeek-V2, the new ultra-wide model uses the same basic architecture around multi-head latent attention (MLA) And DeepSeekMoE. This approach ensures efficient training and inference is maintained – with specialized, shared “experts” (smaller individual neural networks within a larger model) activating 37B of 671B parameters for each token.
While the core architecture ensures robust performance for DeepSeek-V3, the company has also launched two innovations to push the bar even further.
The first is a lossless auxiliary load balancing strategy. This dynamically monitors and adjusts the load of experts to use them in a balanced manner without compromising the overall performance of the model. The second is multi-token prediction (MTP), which allows the model to predict multiple future tokens simultaneously. This innovation not only improves training efficiency, but allows the model to run three times faster, generating 60 tokens per second.
“During pre-training, we trained DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8T high-quality and diverse tokens… Then we performed a two-stage context length extension for DeepSeek-V3,” the company wrote in a statement. technical document detailing the new model. “In the first stage, the maximum context length is extended to 32 KB, and in the second stage it is further extended to 128 KB. Following this, we performed post-training, including supervised fine-tuning ( SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) on the base model of DeepSeek-V3, to align it with human preferences and further unlock its potential. During the post-training phase, we distill the reasoning ability of the DeepSeekR1 Model Serieswhile carefully maintaining the balance between model accuracy and generation time.
Notably, during the training phase, DeepSeek used several hardware and algorithmic optimizations, including the FP8 mixed-precision training framework and the DualPipe algorithm for pipeline parallelism, to reduce process costs.
Overall, it claims to have completed the entire DeepSeek-V3 training in approximately 2,788,000 H800 GPU hours, or approximately $5.57 million, assuming a rental price of $2 per GPU hour. This is far less than the hundreds of millions of dollars typically spent on pre-training large language models.
Llama-3.1, for example, was reportedly trained with an investment of over $500 million.
The most powerful open source model currently available
Despite the economical formation, DeepSeek-V3 has become the most powerful open source model on the market.
The company ran several benchmark tests to compare the AI’s performance and noted that it convincingly outperformed leading open models, including Llama-3.1-405B and Qwen 2.5-72B. It even outperforms closed source code GPT-4o on most benchmarks, except for the English-focused SimpleQA and FRAMES, where the OpenAI model led with scores of 38.2 and 80.5 (compared to 24.9 and 73.3), respectively.
Notably, DeepSeek-V3’s performance particularly stood out on Chinese and math-centric benchmarks, achieving better results than all their counterparts. On the Math-500 test, he scored 90.2, with Qwen’s score of 80 being the second best.
The only model that managed to challenge DeepSeek-V3 was Claudius 3.5 Anthropic Sonnetsurpassing it with higher scores in MMLU-Pro, IF-Eval, GPQA-Diamond, SWE Verified and Aider-Edit.
🚀 Introducing DeepSeek-V3!
— DeepSeek (@deepseek_ai) December 26, 2024
Biggest leap forward yet:
⚡ 60 tokens/second (3x faster than V2!)
💪 Enhanced capabilities
🛠 API compatibility intact
🌍 Fully open-source models & papers
🐋 1/n pic.twitter.com/p1dV9gJ2Sd
The work shows that open source approaches closed models, promising almost equivalent performance in different tasks. Developing such systems is extremely beneficial to the industry as it potentially eliminates the chances of a big AI player running the game. It also gives businesses multiple options to choose from and use while orchestrating their stacks.
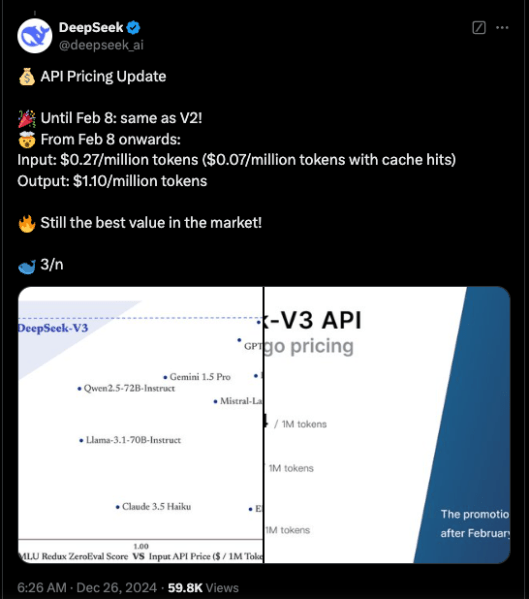
Currently, the code for DeepSeek-V3 is available via GitHub under the MIT license, while the model is provided under the company’s model license. Businesses can also test the new model via In-depth discussiona ChatGPT type platform, and access the API for commercial purposes. DeepSeek provides the API to same price as DeepSeek-V2 until February 8. After that, it will charge $0.27/million input tokens ($0.07/million tokens with cache access) and $1.10/million output tokens.